Measuring the Real Cost of Third-Party Scripts
Overview
The Challenge
Measuring the impact of removing a single third-party library without running experiments in production.
The Solution
A locally run app that repeatedly benchmarked page load times until a confident average could be calculated.
Impact
- Enabled marketing to consider page-load impact when evaluating third-party tools
- Determined that the Facebook Tracking JS had the biggest impact on page load times
- Prompted engineering to defer or lazy-load libraries
- Debunked the belief that bundle size was the only meaningful performance metric
Technical Approach
Architecture
An Electron backend with a simple jQuery front-end.
Tech Stack
Challenges & Solutions
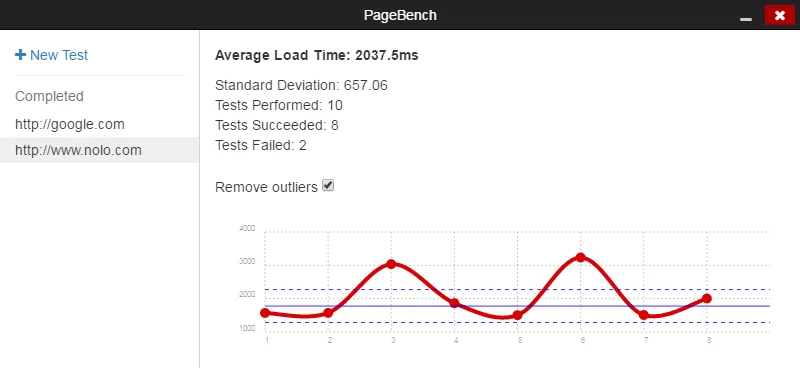
Statistically Significant Timings
Running a handful of tests yielded highly variable load times. To be able to effectively compare load times before and after making a change, tests needed to be repeated until a confidence threshold was reached. The app calculated this dynamically while also removing outliers.
Network Latency
Running the tests at different times of the day resulted in a higher variance of response times. To some, this was an important factor. The solution was to run tests against a local server and download third-party libraries so they were served from the same server. This enabled two testing modes: CPU-only impact, or combined CPU and network impact.
Extracting Performance Timings
An iframe can only be manipulated when the origin is the same. To get around this, tests were conducted inside a <webview> tag. This allowed content scripts to be injected, returning window.performance timings to the parent frame.
Configuring a Test
A list of third-party tracking URLs was embedded in the app. Once the user entered the URL they wanted to test, the Electron backend opened a separate frame that intercepted each network request and compared it against a list of known hosts. This allowed the user to be presented with a list of detected libraries that could be selectively disabled for each test.